- Home >
- Hypothetico-Deductive Method
Hypothetico-Deductive Method
The hypothetico-deductive method is one of the mainstays of scientific research, often regarded as the only 'true' scientific research method.
This article is a part of the guide:
Browse Full Outline
This area fuels intense debate and discussion between many fields of scientific specialization.
Concisely, the method involves the traditional steps of observing the subject, in order to elaborate upon an area of study. This allows the researcher to generate a testable and realistic hypothesis.
The hypothesis must be falsifiable by recognized scientific methods but can never be fully confirmed, because refined research methods may disprove it at a later date.
From the hypothesis, the researcher must generate some initial predictions, which can be proved, or disproved, by the experimental process. These predictions must be inherently testable for the hypothetico-deductive method to be a valid process.
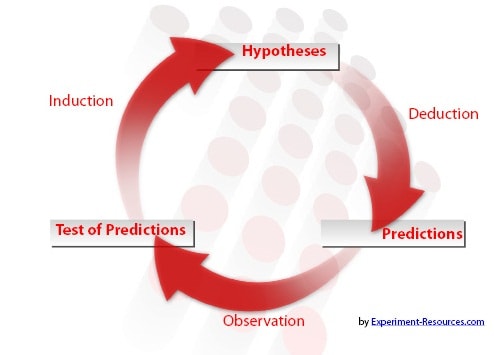
For example, trying to test the hypothesis that God exists would be difficult, because there is no scientific way to evaluate it.

Generating and Analyzing the Data
The next stage is to perform the experiment, obtaining statistically testable results, which can be used to analyze the results and determine whether the hypothesis has validity or has little foundation. This experiment must involve some manipulation of variables to allow the generation of analyzable data.
Finally, statistical tests will confirm whether the predictions are correct or not. This method is usually so rigorous that it is rare for a hypothesis to be completely proved, but some of the initial predictions may be correct and will lead to new areas of research and refinements of the hypothesis.
Assessing the Validity of the Hypothesis
Proving and confirming a hypothesis is never a clear-cut and definitive process. Statistics is a science based on probability, and however strong the results generated; there is always a chance of experimental error.
In addition, there may be another unknown reason that explains the results. Most theories, however solid the proof, develop and evolve over time, changing and adapting as new research refines the known data.
Proving a hypothesis is never completely accurate but, after a process of debate and retesting of the results, may become a scientific assumption. Science is built upon these 'paradigms' and even commonly accepted views may prove to be inaccurate upon further exploration.
A false hypothesis does not necessarily mean that the area of research is now closed or incorrect. The experiment may not have been accurate enough, or there may have been some other contributing error.
This is why the hypothetico-deductive method relies on initial predictions; very few hypotheses, if the research is thorough, are completely wrong as they generate new directions for future research.
Martyn Shuttleworth (Oct 10, 2008). Hypothetico-Deductive Method. Retrieved Feb 25, 2026 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/hypothetico-deductive-method
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
This article is a part of the guide:
Browse Full Outline
Footer bottom



